What is a process?
A process provides resources needed to execute a program. This includes virtual address space, executable code, open handles to system objects, process identifier, and more. A process is basically a container that houses all the resources needed to run a program.
What is a thread?
A thread is a basic unit of which the OS will allocate processor time. In simple terms a thread can execute any part of a process's code. A thread can execute code that another thread is already executing.
What is a handle?
A object in windows is a data structure that represents a system resource. This can be a file, thread, process, or a graphic image. You can not access the information directly in memory, you need to get a handle to that object. This handle gives you access to the information relating to that object but you do have have direct access to the memory of that object. Think handles as the middle man between you and the resource you want to access. Handles will make more sense when you actually need to use them.
What is virtual address space?
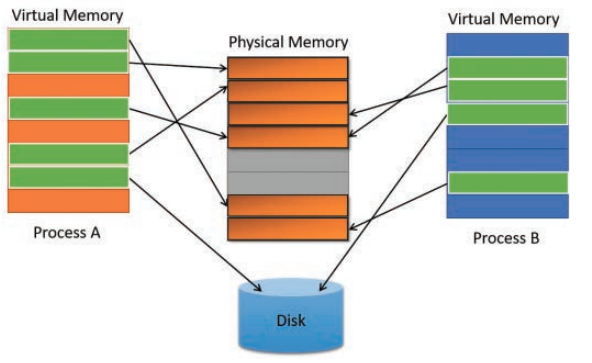
When you start a process it is given a virtual address space. These address are not real RAM addresses but instead map to a real RAM address. The following diagram shows how two processes are sharing the same block of physical memory but in their virtual memory they think they are all alone.
Working with the Win32 API
What is the Win32 API?
The Win32 API is a set of tools that allow programs to interact with the Windows operating system. With the Win32 API you can do a variety of things like create windows, respond to mouse clicks and keystrokes, read and write files, communicate with other processes, and many more.
Creating a simple message box
One of the simplest things you can do in the win32 API is create a message box like the one below

To create a message box you must call the MessageBoxA function in the Win32 API. You can view it's documentation here
The following is the syntax to the function
int MessageBoxA(
[in, optional] HWND hWnd,
[in, optional] LPCSTR lpText,
[in, optional] LPCSTR lpCaption,
[in] UINT uType
);
Let's break down the parameters. First it specifies if a parameter is giving input or output and mention if it's optional. For the first one its [in, optional] this means that parameter is giving input to the function and is optional.
Next they specify the type of the parameter. For the first one it's a type of HWNDthis just means a handle to a window but shorted. For the 2nd and 3rd one it's a LPCSTR this means long pointer constant string (so basically a string). The last one is a UINT which is just a unsigned integer.
Then they lastly just say the name of the parameter. Which does give information on what it is. If a parameter is a handle it always starts with a lowercase 'h'.
The following is a valid way to call MessageBoxA
You may also notice that there is also a MessageBoxExA function. The Ex means extended functionality. That means it can do more and means you will probably need to give more parameters.
The 'A' in MessageBoxA and MessageBoxExA means that strings will be encoded in ANSI a 8 bit encoding standard. If you see 'W' like in MessageBoxW that means that your strings will be encoded in a wide standard 16 bits (unicode). With they wide standard you can support more languages because you have more bits to represent symbols. If you just call MessageBox it will just call MessageBoxA.
All of this knowledge applies everywhere in the windows API but it's easiest to learn it with Message boxes.
Creating a process
You can create a process by running the CreateProcessA function in the windows API. You can the read the documentation of the function here
The following is the syntax of the CreateProcessA function
BOOL CreateProcessA(
[in, optional] LPCSTR lpApplicationName,
[in, out, optional] LPSTR lpCommandLine,
[in, optional] LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpProcessAttributes,
[in, optional] LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpThreadAttributes,
[in] BOOL bInheritHandles,
[in] DWORD dwCreationFlags,
[in, optional] LPVOID lpEnvironment,
[in, optional] LPCSTR lpCurrentDirectory,
[in] LPSTARTUPINFOA lpStartupInfo,
[out] LPPROCESS_INFORMATION lpProcessInformation
);
The following will create a process of notepad
STARTUPINFO si = {0};
si.cb = sizeof(si);
PROCESS_INFORMATION pi = {0};
CreateProcessA(
"C:\\Windows\\System32\\notepad.exe",
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
False,
0,
NULL,
NULL,
&si,
&pi
);
Now try to open a process using the windows API. Try to use the windows API documentation to find out how you can do that (you will be doing that A LOT)